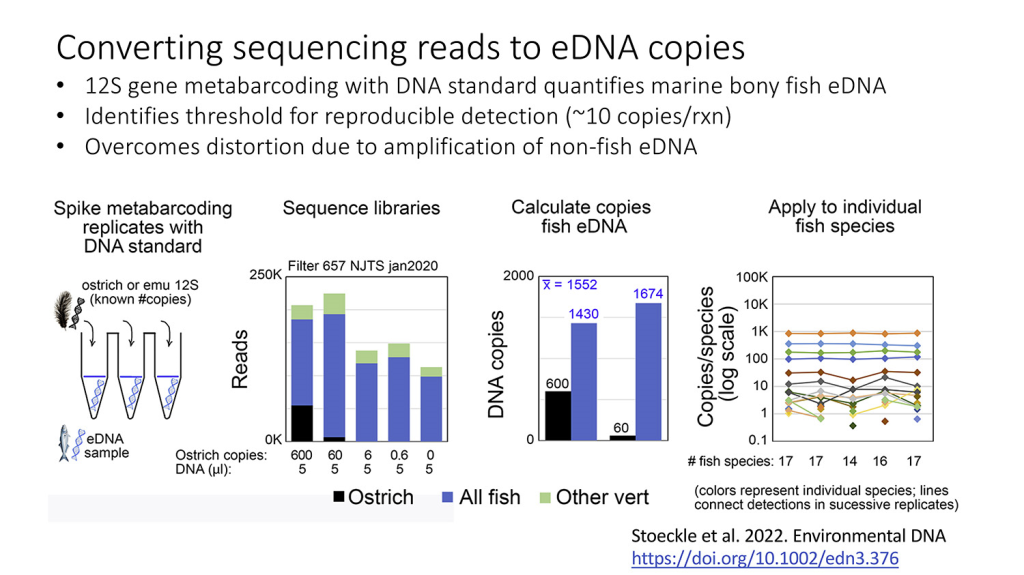
Swiss bioinformatics wizard Wandrille Duchemin and PHE Guest Investigator David Thaler publish PyKleeBarcode: Enabling representation of the whole animal kingdom in information space in PLoS One. The computational advances in the paper open the way to calculating DNA-relatedness of all animal species, as the figure below for mammals suggests.
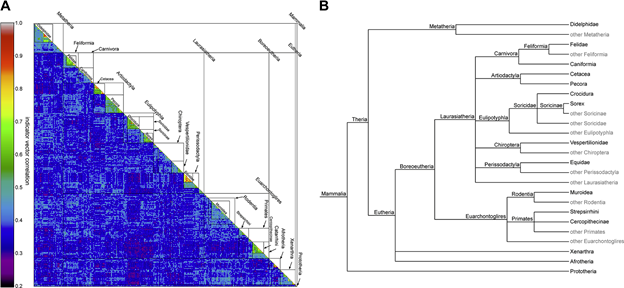
Fig 2. A. View of the structure matrix of the mammalian dataset and taxonomic structure of Mammalia. B. Phylogenetic tree structure of the taxonomic groups retrieved from NCBI taxonomy.
The paper builds on the pioneering work done earlier in the PHE by Larry Sirovich and Mark Stoeckle:
L Sirovich, MY Stoeckle, Y Zhang. A scalable method for analysis and display of DNA sequences. PLoS ONE 4 (10): e7051, 2009
L Sirovich, MY Stoeckle, Y Zhang. Structural analysis of biodiversity. PLoS ONE 5 (2): e9266, 2010
MY Stoeckle, C Coffran. TreeParser-Aided Klee Diagrams Display Taxonomic Clusters in DNA Barcode and Nuclear Gene Datasets . Nature Scientific Reports 3 (2635): 2013