Next: Decomposition
Up: The Mathematics of Loglet
Previous: The Mathematics of Loglet
Contents
Consider the two-dimensional space in which our data set 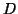 exists. If
there are
exists. If
there are 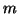 data points, then we define
data points, then we define 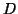 as
where
as
where 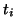 usually represents time, while
usually represents time, while 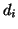 represents the
growing variable (e.g., number of organisms, percent of saturation).
represents the
growing variable (e.g., number of organisms, percent of saturation).
Suppose we want to fit a logistic curve of 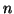 components to the model.
Then we will require
components to the model.
Then we will require 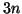 parameters, represented as a
parameters, represented as a
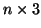 matrix
matrix
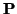 , where the
, where the 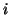 th row describes the
th row describes the 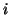 th component:
th component:
Thus a loglet can be alternatively specified by
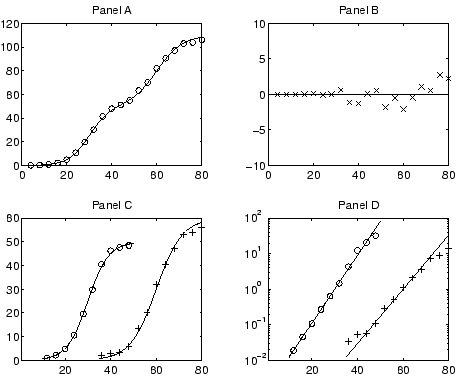
Figure 5A shows a hypothetical data set
(the circles) and a fitted loglet with 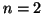 and
and
Gaussian noise was added to the data to dataset to show the residuals.
Figure 5:
A hypothetical bi-logistic data set(A), the residuals of the
fitted curve(B), and the decompositions in raw form (C) and
with the Fisher-Pry transform applied (D).
|
|




Next: Decomposition
Up: The Mathematics of Loglet
Previous: The Mathematics of Loglet
Contents
Jason Yung
2004-01-28
![]() components to the model.
Then we will require
components to the model.
Then we will require ![]() parameters, represented as a
parameters, represented as a
![]() matrix
matrix
![]() , where the
, where the ![]() th row describes the
th row describes the ![]() th component:
th component:
![]() and
and
![$\displaystyle \bold P = \left[ \begin{array}{ccc}
20 & 50 & 30 \\
25 & 60 & 60 \end{array} \right].$](img52.png)