Exploring unicellular eukaryotic universe with mtDNA
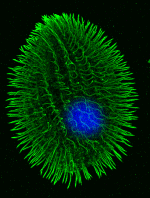 Most DNA barcode research to date analyzes multicellular animals, but why stop there? Unicellular eukaryotes or “protists” probably comprise most of Earth’s biomass and encompass more genetic diversity than all multicellular animals and plants combined. In current J Eukaryot Microbiol 2006 53:385 Denis Lynn and Michaela Struder-Kypke report on mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I sequences in Tetrahymena, a ciliate protozoan genus related to Paramecium which includes T. thermophila, a model organism and the first free-living unicellular eukaryote genome sequenced. The authors analyzed 14 isolates of T. thermophila from 2 geographically distant locations, and 4 pairs of Tetrahymena sister species selected because they show NO sequence difference in nuclear small subunit ribsomal (SSrRNA) genes. They found less than 1% intraspecific sequence variation within T. thermophila isolates. Differences between species ranged from 1%-12% and the sister species pairs which have identical SSrRNA genes showed differences in mtCOI sequences.
Most DNA barcode research to date analyzes multicellular animals, but why stop there? Unicellular eukaryotes or “protists” probably comprise most of Earth’s biomass and encompass more genetic diversity than all multicellular animals and plants combined. In current J Eukaryot Microbiol 2006 53:385 Denis Lynn and Michaela Struder-Kypke report on mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I sequences in Tetrahymena, a ciliate protozoan genus related to Paramecium which includes T. thermophila, a model organism and the first free-living unicellular eukaryote genome sequenced. The authors analyzed 14 isolates of T. thermophila from 2 geographically distant locations, and 4 pairs of Tetrahymena sister species selected because they show NO sequence difference in nuclear small subunit ribsomal (SSrRNA) genes. They found less than 1% intraspecific sequence variation within T. thermophila isolates. Differences between species ranged from 1%-12% and the sister species pairs which have identical SSrRNA genes showed differences in mtCOI sequences. 
This early study suggests further exploration of unicellular eukaryotic biodiversity with COI barcodes will be fruitful.
This entry was posted on Thursday, September 14th, 2006 at 11:02 am and is filed under General. You can follow any responses to this entry through the RSS 2.0 feed. Both comments and pings are currently closed.